What is forex trading?
Forex, also known as foreign exchange or FX trading, is the conversion of one currency into another. Take a closer look at everything you’ll need to know about forex, including what it is, how you trade it and how leverage in forex works.

What is forex trading?
Forex trading is the means through which one currency is changed into another. When trading forex, you are always trading a currency pair—selling one currency while simultaneously buying another.
Each currency in the pair is listed as a three-letter code, which tends to be formed of two letters that stand for the region, and one standing for the currency itself.
Example: USD stands for the US dollar and JPY for the Japanese yen. In the USD/JPY pair, you are buying the US dollar by selling the Japanese yen.
To keep things ordered, most providers split pairs into categories.
FOUR TYPES OF FOREX PAIRS:
- Major pairs -seven currencies that makeup 80% of global forex trading. Includes EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD and USD/CHF
- Minor pairs - less frequently traded, these often feature major currencies against each other instead of the US dollar. Includes: GBP/CAD, EUR/CHF, GBP/JPY
- Exotics pairs- a major currency against one from a small or emerging economy. Includes: USD/MXN, EUR/ZAR, GBP/SGD
- Regional pairs - pairs classified by region – such as Scandinavia or Australasia. Includes: EUR/NOK, AUD/NZD, AUD/SGD
Most forex transactions are carried out by banks or individuals by seeking to buy a currency that will increase in value against the currency they sell. However, if you have ever converted one currency into another, for example, when traveling, you have made a forex transaction.
How does forex trading work?
Institutional forex trading takes place directly between two parties in an over-the-counter (OTC) market. Meaning there are no centralized exchanges (like the stock market), and the institutional forex market is instead run by a global network of banks and other organizations.
Transactions are spread across four major forex trading centers in different time zones: London, New York, Sydney, and Tokyo. Since there is no centralized location, you can trade forex 24 hours a day.
Most traders speculating on forex prices do not take delivery of the currency itself. Instead, traders will make exchange rate predictions to take advantage of price movements in the market. The most popular way of doing this is by trading derivatives, such as a rolling spot forex contract offered by tastyfx.
Trading derivatives allows you to speculate on an asset’s price movements without taking ownership of that asset. For instance, when trading forex with tastyfx, you can predict on the direction in which you think a currency pair’s price will move. The extent to which your prediction is correct determines your profit or loss.
THE THREE DIFFERENT TYPES OF FOREX MARKET:
- Spot forex market: the physical exchange of a currency pair, which takes place at the exact point the trade is settled – ie ‘on the spot’ – or within a short period of time. Derivatives based on the spot forex market are offered over-the-counter by dealers like tastyfx.
- Forward forex market: a contract is agreeing to buy or sell a set amount of a currency at a specified price, and to be settled at a set date in the future or within a range of future dates
- Futures forex market: an exchange-traded contract to buy or sell a set amount of a given currency at a set price and date in the future.
FOREX PRICING—BASE AND QUOTE CURRENCY
The first currency listed in a forex pair is called the base currency, and the second currency is called the quote currency. The price of a forex pair is how much one unit of the base currency is worth in the quote currency.

In the above example, GBP is the base currency and USD is the quote currency. If GBP/USD is trading at 1.35361, then one pound is worth 1.35361 dollars.
If the pound rises against the dollar, then a single pound will be worth more dollars and the pair’s price will increase. If it drops, the pair’s price will decrease. So, if you think that the base currency in a pair is likely to strengthen against the quote currency, you can buy the pair (going long). If you think it will weaken, you can sell the pair (going short).
What is leverage in forex trading?
A key advantage of spot forex is the ability to open a position on leverage. Leverage allows you to increase your exposure to a financial market without having to commit as much capital.
When trading with leverage, you don’t need to pay the full value of your trade upfront. Instead, you put down a small deposit, known as margin. When you close a leveraged position, your profit or loss is based on the full size of the trade.
This means that leverage can magnify your profits, but it also brings the risk of amplified losses—including losses that can exceed your initial deposit. Leveraged trading, therefore, makes it extremely important to learn how to manage your risk.
What is margin in forex trading?
Margin is a key part of leveraged trading. It is the term used to describe the initial deposit you put up to open and maintain a leveraged position. When you are trading forex with margin, remember that your margin requirement will change depending on your broker, and how large your trade size is.
Margin is usually expressed as a percentage of the full position. So, a trade on EUR/USD, for instance, might only require a deposit of 2% of the total value of the position for it to be opened. Meaning that while you are still risking $10,000, you’d only need to deposit $200 to get the full exposure.
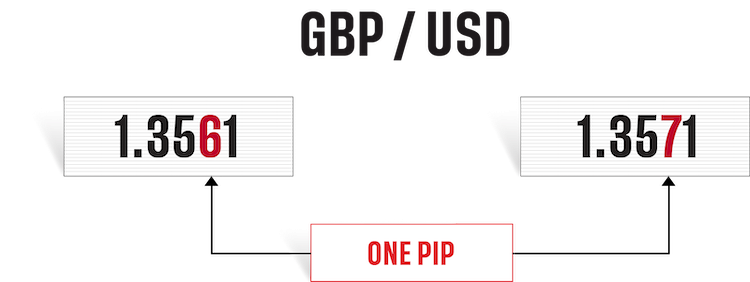
What is a pip in forex trading?
Pips are the units used to measure movement in a forex pair. A forex pip usually refers to a movement in the fourth decimal place of a currency pair. So, if EUR/USD moves from $1.35361 to $1.35371, then it has moved a single pip. The decimal places that are shown after the pip are called micro pips, or sometimes pipettes, and represent a fraction of a pip.
The exception to this rule is when the quote currency is listed in much smaller denominations, with the most notable example being the Japanese yen. Here, a movement in the second decimal place constitutes a single pip. So, if EUR/JPY moves from ¥172.119 to ¥172.129, it has moved a single pip.

What is the spread in forex trading?
In forex trading, the spread is the difference between the buy and sell prices quoted for a forex pair. If, for instance, the buy price on EUR/USD was 1.7645 and the sell price was 1.7649, the spread would be four pips.
If you want to open a long position, you trade at the buy price, which is slightly above the market price. If you want to open a short position, you trade at the sell price—slightly below the market price.
tastyfx offers competitive spreads of 0.8 pips for EUR/USD and USD/JPY, and 1 pip on GBP/USD, AUD/USD and EUR/GBP.
What is a lot in forex trading?
Currencies are traded in lots—batches of currency used to standardize forex trades. In forex trading, a standard lot is 100,000 units of currency. Alternatively, you can sometimes trade mini lots and micro lots, worth 10,000 and 1000 units respectively
Individual traders don’t necessarily have 100,000 dollars, pounds or euros to place on every trade, so many forex trading providers like tastyfx offer leveraged products that allow traders to open a full lot of EUR/USD for only euro sign 2000 of initial margin.
What moves the forex market?
Like most financial markets, forex is primarily driven by the forces of supply and demand, and it is important to gain an understanding of the influences that drive these factors.

CENTRAL BANKS
Supply is controlled by central banks, who can announce measures that will have a significant effect on their currency’s price. Quantitative easing, for instance, involves injecting more money into an economy, and can cause its currency’s price to drop.
Central banks also control the base interest rate for an economy.
If you purchase an asset in a currency that has a high interest rate, you may get higher returns. This can make investors flock to a country that has recently raised interest rates, in turn boosting its economy and driving up its currency.
However, higher interest rates can also make borrowing money harder. If money is more expensive to borrow, investing is harder, and currencies may weaken.
NEWS REPORTS
Commercial banks and other investors tend to want to put their capital into economies that have a strong outlook. So, if a positive piece of news hits the markets about a certain region, it will encourage investment and increase demand for that region’s currency.
Unless there is a parallel increase in supply for the currency, the disparity between supply and demand will cause its price to increase. Similarly, a piece of negative news can cause investment to decrease and lower a currency’s price. As a result, currencies tend to reflect the reported economic health of the country or region that they represent.
Take a look at our economic calendar to see what’s ahead, and pay particular attention to:
- Inflation figures
- GDP
- Production reports
- Retail sales
- Employment
MARKET SENTIMENT
Market sentiment, which is often in reaction to the news, can also play a major role in driving currency prices. If traders believe that a currency is headed in a certain direction, they will trade accordingly and may convince others to follow suit, increasing or decreasing demand.
.jpg?format=pjpg&auto=webp&quality=90)
.jpg?format=pjpg&auto=webp&quality=90)
Discover forex trading with tastyfx
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Despite the enormous size of the forex market, there is very little regulation since there is no governing body to police it 24/7. Instead, there are several national trading bodies around the world who supervise domestic forex trading, as well as other markets, to ensure that all forex providers adhere to certain standards.
In America, the two primary agencies responsible for regulating the forex market are the Commodity Futures Trade Commission (CFTC) and the National Futures Association.
Approximately $5 trillion worth of forex transactions take place daily, which is an average of $220 billion per hour.1 The market is largely made up of institutions, corporations, governments and currency speculators. Speculation makes up roughly 90% of trading volume, and a large majority of this is concentrated on the US dollar, euro and yen.
Gaps are points in a market when there is a sharp movement up or down with little or no trading in between, resulting in a ‘gap’ in the normal price pattern. Gaps do occur in the forex market, but they are significantly less common than in other markets because forex is traded 24 hours a day, five days a week.
However, gapping can occur when economic data is released that comes as a surprise to markets, or when trading resumes after the weekend or a holiday. Although the forex market is closed to speculative trading over the weekend, the market is still open to central banks and related organizations. So, it is possible that the opening price on a Monday morning will be different from the closing price on the previous Saturday morning—resulting in a gap.
The cost of trading forex depends on which currency pairs you choose to buy or sell. With tastyfx, you’ll trade forex on margin, which means you need a small percentage of the full value of the trade to open and maintain your position. Margin isn’t a direct cost to you, but it has a significant impact on the affordability of your trade.
Other than the margin, you also pay a spread, which is the difference between the ‘buy’ and the ‘sell’ price of an asset. To open a long position, you’d trade slightly above the market price (buy price) and to open a short position, you’d trade slightly below the market price (sell price).
Lastly, if you do not close your position before the end of the trading day, you will pay overnight funding charges.
The best time to trade forex will depend on your personal risk preference, as high liquidity and volatility can affect forex prices. When the London session opens at 3am (EST), liquidity and volatility will likely be high as traders begin interacting with each other. Trading will usually become less liquid a few hours later, and it will pick up again after the American session opens at around 9:30 am (EST).
The foreign exchange market is open 24 hours a day, five days a week—from 3`am Sunday to 5pm Friday (EST). So, you can trade at a time that suits you and take advantage of different active sessions.
Remember: the forex market’s opening hours will change when certain countries shift to daylight savings time.
With tastyfx, you can open a forex trading account online, call (312) 981-0498, or email helpdesk.us@tastyfx.com. There’s no obligation to add funds until you want to place a trade.
Alternatively, you can open a demo account to experience our award-winning platform2 and develop your forex trading skills.
1 The greater foreign exchange marketplace reached $7.5 trillion per day in 2022, however, tastyfx LLC is the counterparty to the FX transactions of its client base and therefore serves as the liquidity provider in this much smaller subsection of this marketplace. Source: Bank for International Settlements Triennial Central Bank Survey (2022).
2 #1 Overall Broker, #1 Mobile App, #1 Trust Score, #1 Education, #1 Web Platform are accolades presented to IG, parent company of tastyfx, on January 28, 2025, during the ForexBrokers.com 2025 Annual Awards. Accolades were awarded by the ForexBrokers.com research team based on demonstrated excellence in categories considered important to investors, traders, and consumers. Click here to learn about how they rate brokers.