What factors affect the value of the US dollar?
There are various socio-political and economic factors that cause the rise and fall of the US dollar price. Discover factors impacting the dollar price in an ever-changing global economy.

What impacts the value of the dollar?
There are six fundamental factors that have an influence on the US dollar exchange rate. These include things such as economic performance, supply and demand of currency, inflation and geopolitical factors. More of these are detailed below.
Moves in the federal funds rate
The federal funds rate is the interest rate commercial banks lend extra reserves to one another on an overnight basis. The target rate is set by the Federal Reserve’s Open Market Committee (FOMC), and it serves as the base interest rate to control the supply of money in America.1
Regulations governing commercial banks in the US require that a certain percentage of total funds deposited are held in reserves. This serves as assurance towards the bank’s financial stability and solvency.1
In a constantly changing environment, banks may find themselves in excess or shortfall of the required daily reserves. When in a shortfall of reserves, banks take out overnight loans from their peers. And when in excess banks will also lend to their peers.1
The federal funds rate has an impact on inflation, short-and long-term interest rates, as well as foreign currency exchange rates – and is used to bring these costs under control. The higher the federal funds rate, the more expensive bank loans, home loans or mortgages and credit cards will cost to pay back.2
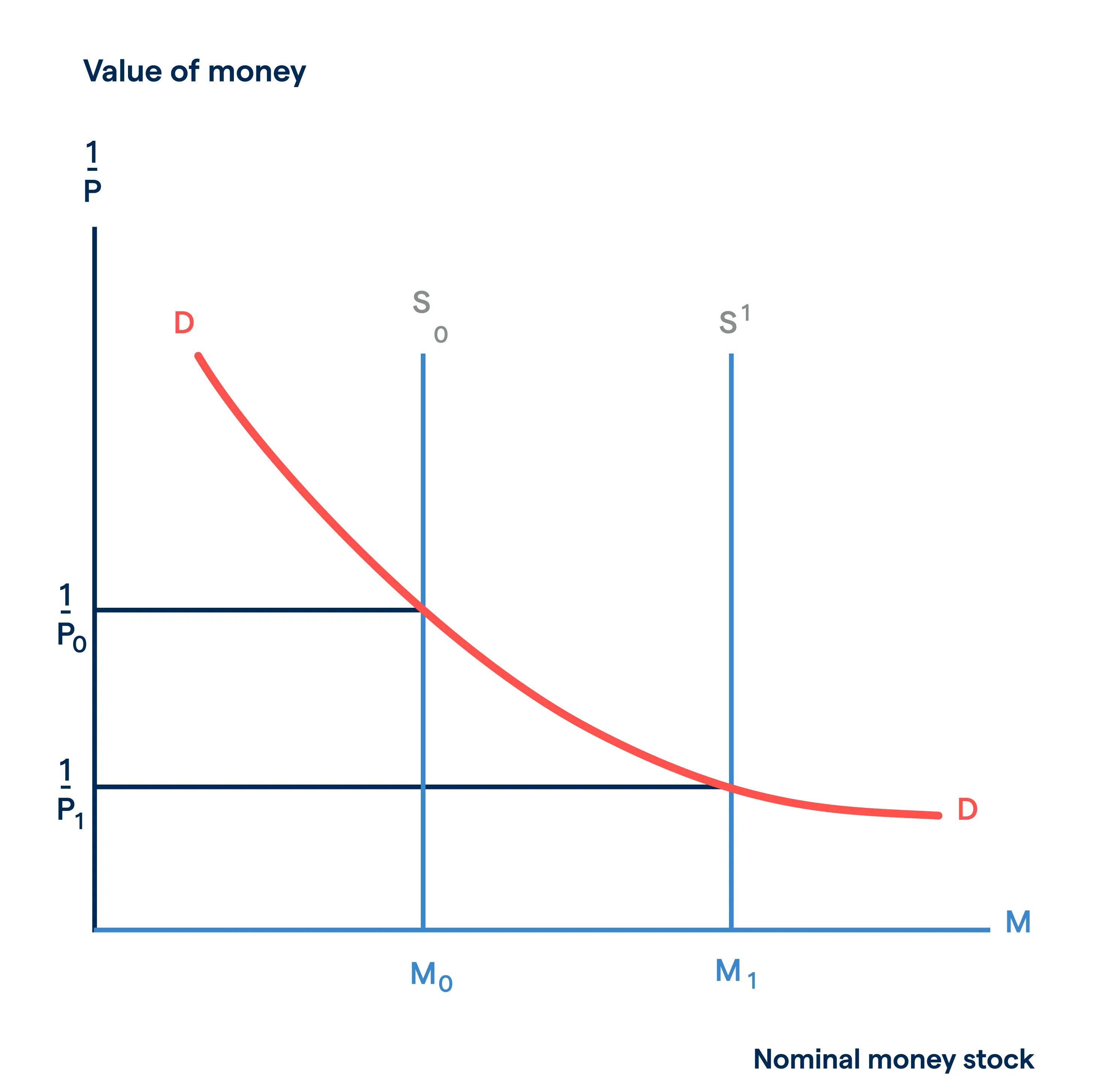
Above and beyond its effect on other interest rates, the federal funds rate also serves as the base interest rate to control the supply of money within the US economy.2 When there’s a higher demand for the US dollar, which often occurs when there’s a short supply of the currency, its monetary value increases.
When the federal funds rate increases, the cost of borrowing also boosts the economy’s wealth, but it also helps bring an end to a rise in inflation.
Demand for currency
The US dollar has been predominantly used as a currency peg. This is when a government policy implements fixed exchange rates for its national currency to that of another country, in this case the US dollar. Some countries that use the US dollar as a medium of exchange include Ecuador, Puerto Rico and Zimbabwe.
Using the US dollar as a dominant currency increases its demand, making it the world’s reserve currency as most countries use it for the global trade of commodities. Central banks and major financial institutions store reserve currencies for use in global transactions and to decrease risks associated with exchange rates.3
However, over the years, another threat to the US dollar’s status as a reserve currency has been other alternative currencies. These are the euro, Japanese yen, British pound sterling, including the smaller reserve currencies like the Canadian dollar and Australian dollar.3
Despite their small market share in the reserve currency, these alternative currencies are slowly eating away at the US dollar’s dominance and might negatively impact the future demand for this currency.3
Inflation
Inflation is the rate at which an economy’s currency loses its purchasing power over time. A weaker dollar would increase the price of imports, leading to a rise in inflation. This would place more pressure on the US economy, that’s currently dealing with rising inflation and potentially restricting consumers from borrowing.3
The government tends to increase the federal funds target rate, subsequently leading to a rise in short-term interest rates. This raises the cost of credit, which increases the economy's wealth as the supply of money is reduced. However, it also deters consumers and businesses from taking out loans, encouraging them to save and potentially earn high interest.4
An economic cycle shows how inflation affects the financial markets. There’s an increase in interest rate when the economy grows and a decrease when the economy contracts.
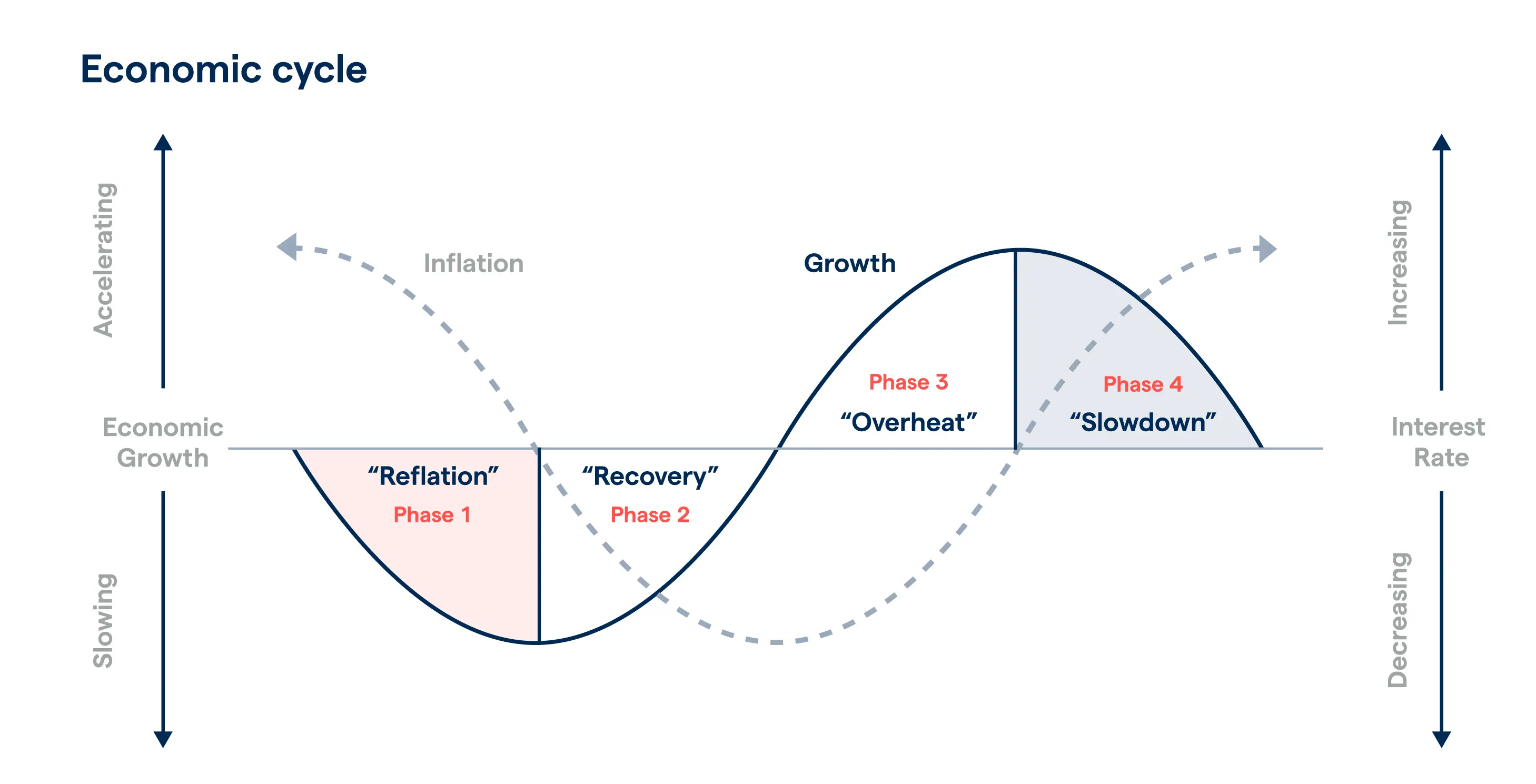
For instance, the cost of a Mars chocolate bar you buy today is likely to be priced higher than it was a year or two ago. Meaning if you buy an item for $10 today, it’ll cost quite a bit more in a year or two.
While this is a simplified example, it does demonstrate the impact inflation has on the consumer’s purchasing power, which is applicable to the cost of both goods and services.
Performance of the US economy
When the US economy performs well, the value of the dollar appreciates. The US dollar showed its resilience post-Covid-19 pandemic bouncing back to its former glory as interest rates increase at a fast pace compared to other global economies.3 Interest rate hikes are often attractive to foreign investors, as they increase earnings when investing in the US dollar.
The opposite would hold true if the US dollar price depreciated due to a weak economic performance. A severe weak dollar would negatively affect global economies. And with the depreciation of the US dollar, other world currencies like the Eurozone, China and Japan will also be devalued since their economic growth heavily rely on exports.3
Learn more about how forex trading works
Trade balances
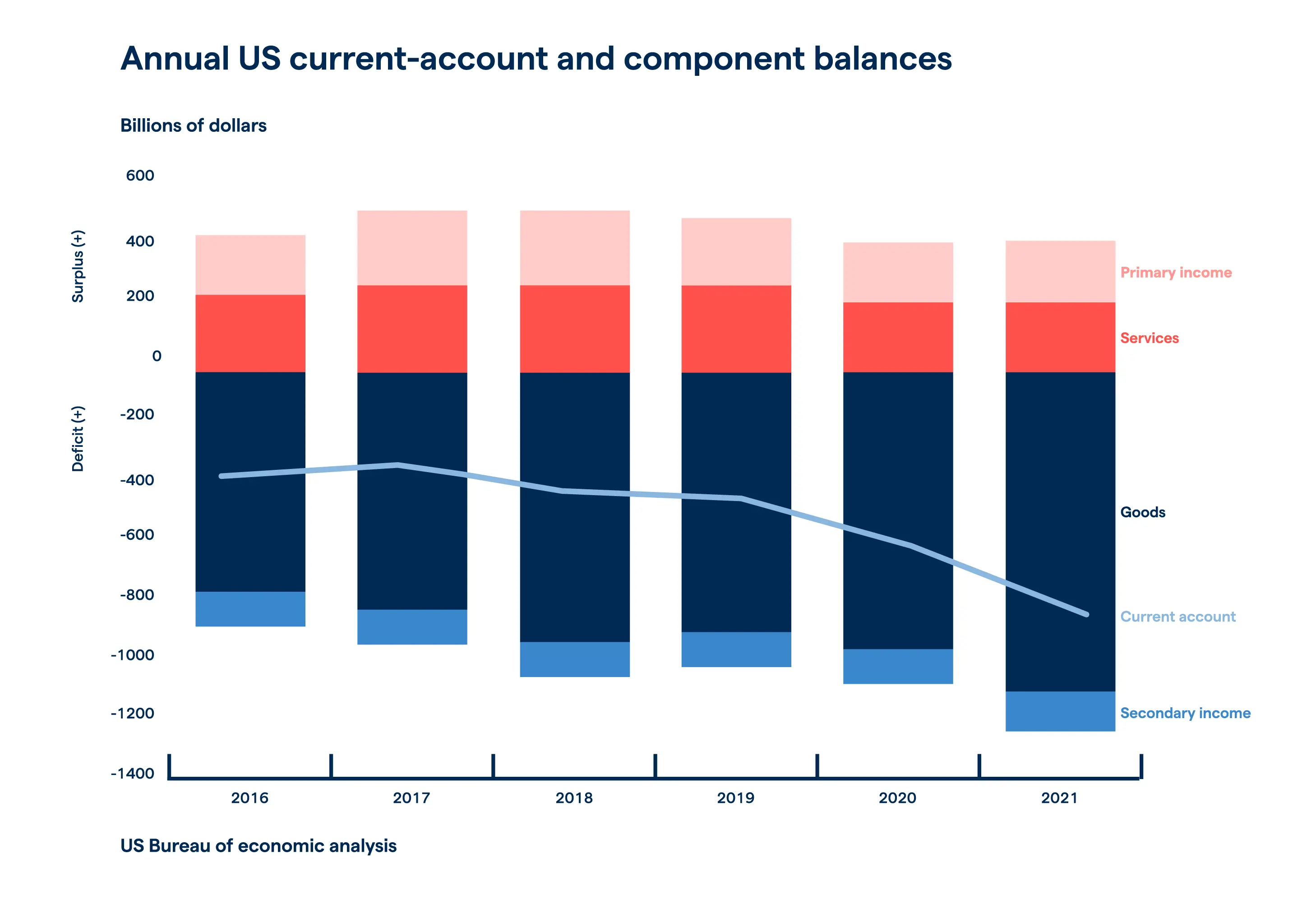
America’s huge current account deficit is one of the biggest threats to the US dollar. Since almost four decades ago, the value of goods and services imported into the US exceeds those being exported. This is reflected in the high inflation, subsequently decreasing the dollar’s value.3
In 2021, the US’s current account deficit increased by 33.4% ($205.5 billion) to $821.6 billion due to its widened shortfall on goods. The US also takes out loans from foreign lenders to finance itself against the deficit. This may have a negative impact on the value of the US dollar price if this global economic leader does not claw its way out of debt.3, 5
Political instability and unpredictable events
When geo-political uncertainty is on the rise, investors tend to move wealth into safer, less volatile currencies that will weather the storm better. There are several of these currencies around the world – with the US dollar being one of them.
The Ukraine-Russia conflict also led to appreciation of the US dollar as investors looked for a safer haven and a more liquid market.6 Since the beginning of the Russian invasion on Ukraine in early 2022 to the start of 2023, the price of the US dollar strengthened.3
This followed the US dollar’s weakened state compared to major currencies like the euro and the pound sterling in the first year of the Covid-19 pandemic. Other major currencies include the Japanese yen, Canadian dollar, Swedish krona and Swiss franc.7
In the 12 months to June 2022, the US dollar price increased by 12% against the euro, 9% against the pound, and 16% against the yen.7
In mid-May of 2022, the dollar’s weighted average value against the world’s six major currencies and appreciated by 9% since February – a 20-year high.7
How to trade on forex and the US dollar
- Choose a currency pair to trade
- Create an account or practice on a demo
- Decide whether to ‘buy’ or ‘sell’
- Take steps to manage your risk
- Open your first trade
- Monitor your position
When trading with leverage, you’ll need to pay an initial deposit called margin to open a position and increase your exposure to your foreign exchange currency of your choice. While leverage can magnify your profits, it’ll amplify your losses and possibly exceed your initial account size.
With us, you can trade the US dollar by choosing a forex pair that includes the American currency. Forex trading involves buying one currency while selling another based on how much each currency is valued on the FX market.
For instance, the current market price of the GBP/USD forex pair shows how many US dollars it would take to buy one pound. Some of the other common forex pairs you can trade are the USD/CAD, USD/CHF, USD/JPY and AUD/USD.
Factors affecting the US dollar price summed up
- The federal funds rate has an impact on inflation, short and long-term interest rates, as well as foreign currency exchange rates and is used to bring these costs under control
- Inflation is the rate at which an economy’s currency loses its purchasing power over time. A weaker dollar would increase the price of imports, which could lead to a rise in inflation
- America’s huge current account deficit is one of the biggest threats to the US dollar
- When geo-political uncertainty is on the rise, investors tend to move wealth into safer, less volatile currencies that will weather the storm better
- The gold price is used as a measure of the US dollar’s value and investor confidence in the currency during times of war and peace
- With us, you can choose to trade major and minor forex pairs
Footnotes
1 Forbes Advisor, 2022
2 Bankrate, 2022
3 CNBC, 2022
4 Forbes, 2022
5 Bureau of Economic Analysis, 2022
6 Financial Times, 2022
7 Econofact, 2022
This information has been prepared by tastyfx, a trading name of tastyfx LLC. This material does not contain a record of our trading prices, or an offer of, or solicitation for, a transaction in any financial instrument. You should not treat any opinion expressed in this material as a specific inducement to make any investment or follow any strategy, but only as an expression of opinion. This material does not consider your investment objectives, financial situation or needs and is not intended as recommendations appropriate for you. No representation or warranty is given as to the accuracy or completeness of the above information. tastyfx accepts no responsibility for any use that may be made of these comments and for any consequences that result. See our Summary Conflicts Policy, available on our website.
